We have made some change and improvement to reduce the size of the electronic board
New industrial Lab for HardSploit production
Thanks to our financial Partners (Region Bretagne @regionbretagne, @BretagneBDI , @lameito…), we succeed to update our electronic production line.
The goal is to be able to produce small series @ Opale Security Lab in a more effective way
- A new stenciling machine & a new oven
As explain on Adafruit Web site,
Stencil machines hold the metal-cut stencil flat and taut so that you dont have any shifting or curling while you try to lay paste down. The good ones have a fixture so you can always get the same alignement every time – speeding up your stenciling time down to under a minute per PCB
We choose A C.I.F machine. See below
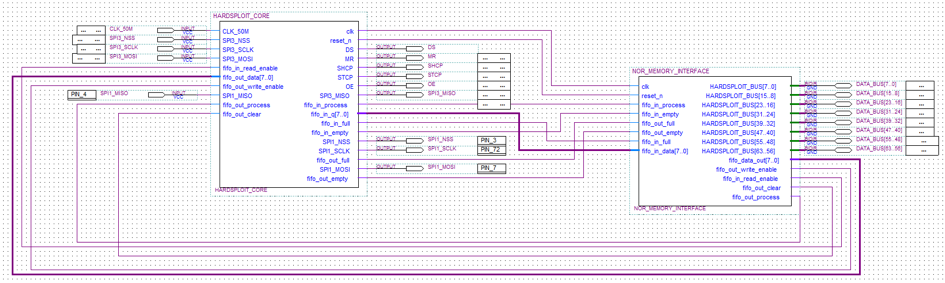
Hardsploit Module : Parallel memory dump
As the Hardsploit Core Framework is over, we continue with the development of Hardsploit modules. A Hardsploit Module is like an Exploit Module for Metasploit. It’s a piece of FPGA code that have a dedicated hacking (or auditing ;-)) function; Each module will offer functionalities such as dump, read & write, interact, Proxy or sniff etc.
To begin, we have designed a module related to parallel memory. Why? Mainly because, to our knowledge, there is no tool that can achieve that in a simple way.
Summary of Hardsploit Internal Communication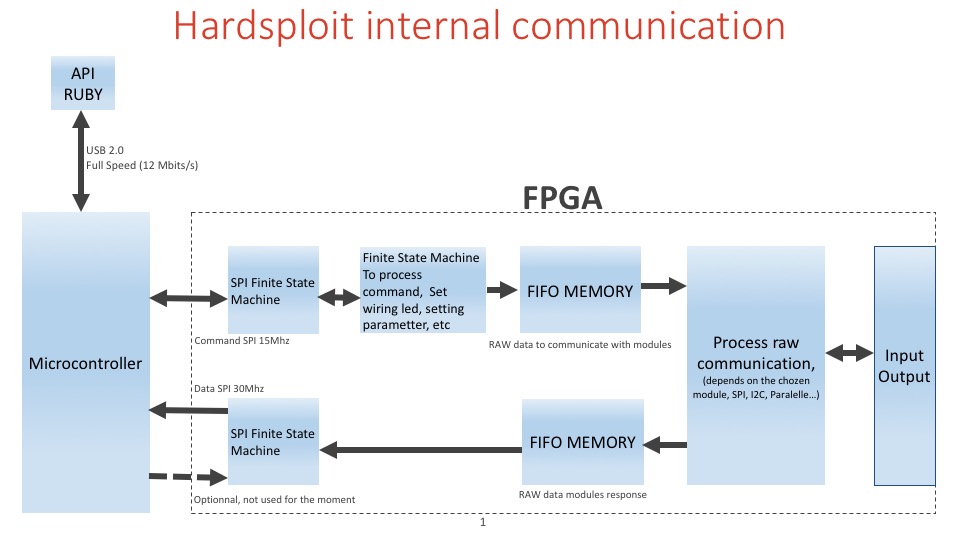
The parallel memory module for example, looks like the following. It will use the Core FPGA Hardsploit module.
Harsploit core module is a bit complicated stuff
- One PLL to obtain 150Mhz from 50 Mhz oscillator.
- The core receive a command by SPI slave
- Set helping wiring functionality
- or fill the FIFO (First In First Out) memory to obtain a raw communication with each module (parallel memory, spi, I2C, 1Wire, etc)
- The module can send information to the second fifo and send the content to the microcontroller (uC) by spi master.
- There are 2 finite state machine to organize all tasks.
- Microcontroller send data to ruby for each receiving data by FPGA by DMA (Direct Access Memory) of the uC.
Simple? 🙂 Maybe a flowchart could help (or not ?)
In brief, we have created a FPGA module that is able to dump most of parallel memory chip. It will help security pentesters to dump firmware or all content contained in such memory in a easy way.
- Easier than if you need to create a dumping wiring function each time … No more arduino like board with plenty of wiring difficulties to connect to your chip, no more trouble to find the right memory command to be able to dump the component in front of you… The GUI will help you achieve that in few click only.
- Faster, as we use High Speed FPGA buses and machine state to achieved the dump.
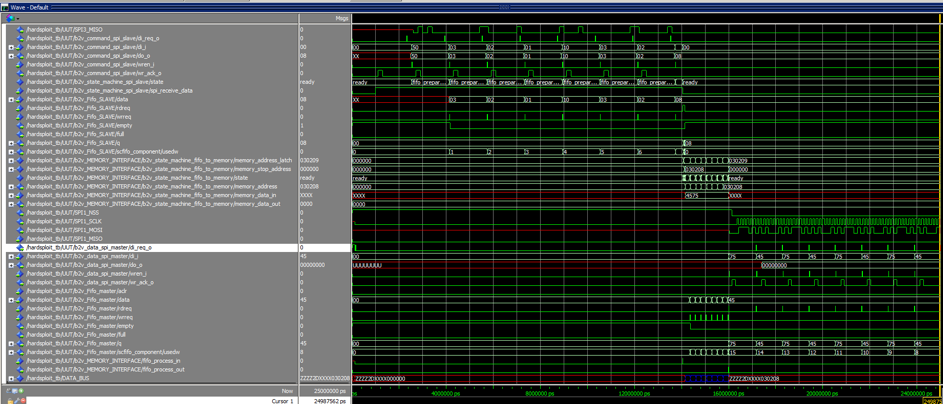
During our simulation and testing step, we succeed to dump parallel memory command with 3x8bits for address (see Graph Below)
What type of Memories we could dump for now?
- 32 bits for address / 8bits data = 4096 M => 4Go max
- 32 bits for address / 16bits data = 2×4096 M => 8Go max
Performance? Dumping Speed achieved (real world example – no bullshit)
For example, a dump of 128MByte memory chip.
- 1st result : only 5 to 10 min to read a embedded linux rom of 128MB.
More on dumping performance, according to our test ,
- Worst speed is 0.2MByte/s means less than 5 hour to read 4Go
- Average speed is 0.5MByte/s means about 2.2 hour for a dump of 4Go
- Max speed is 0.8MByte/s means about 80 min for a dump of 4Go
Just try to achieve that with other existing solution 😉
How to use that funky and (over) hype parallel dumping and writing function ?
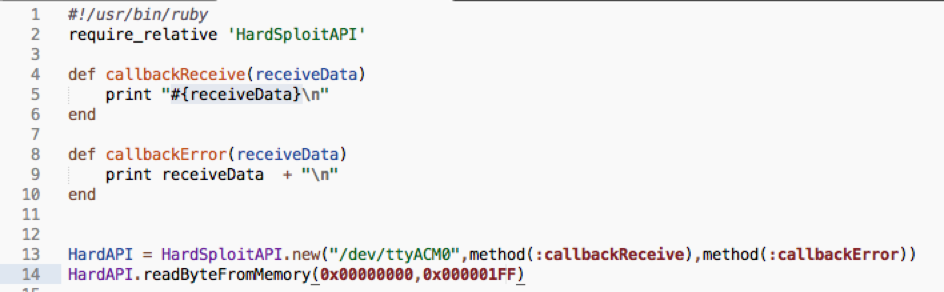
We use our API (soon linked with the GUI…stay tuned)
We create a low level API with ruby that let you interact with FGPA module (Harsploit Module) in a simply way. See below an example of code we use. One function to call , few parameters to send (block to dump), few command to drive the chip. All those parameters will be soon pre input via the use of the GUI.
Results (with testing values – interesting data is at the beginning of the block)
Now you need to reverse the content of this memory and it’s your pentesters’ job 🙂
More information coming soon about several other Hardsploit Modules (I2C, SPI etc…)
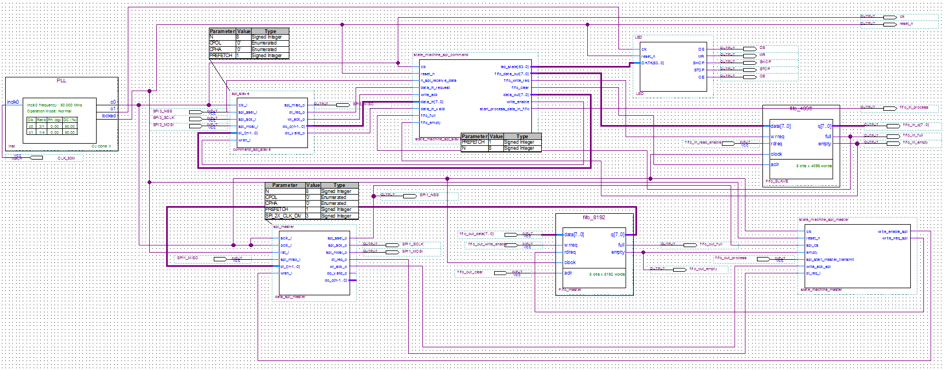
Hardsploit Explained : Internal communication overview
As an image could help to understand how “things” work. Please find below a graphic that shows most of HardSploit Internal communications.
Hardsploit : There’s an app (also) for that ! (update 1)
Because all is not always about PCB, soldering and blinking leds, here is a post with more information about our technological choices concerning the way Harsploit will communicate with higher level layers. You will notice that some choices we’ve made are not necessarily dicted by a given technology but in contrary because it’s seemed fun , useful and interesting to achieve our functional goals : create an easy to use Hardware Hacking Framework !
Here is a graphic summary for those who are in a hurry :
The concept behind Hardsploit when the idea came up was “Make the hardware pentesting more accessible and more flexible”. What we mean by that ? Well, in few clicks you must be able to get the content or hack the electronic components you’re working on. So yes, if it wasn’t already clear in your mind there is a graphical interface, but don’t worry if you are more a command line person we haven’t forgotten you.
Why Ruby in particular ? First thing is, we were interrested to know more about it and then because we realize that it is very “smooth” to use (the gem system is very convenient, the simple syntax even more). No technical reasons here, we are not limited by it, technically speaking, and we hope that will continue this way (apparently no reason the inverse happen).
Is it still necessary to introduce it ? Logic choice for local/client storage, work great with Ruby and perfect system interoperability.
No doubt one of the most useful thing we use with Ruby. Define the database model, forget raw SQL. An invaluable time saving. As a security company that perform application pentesting we are still curious to know how it handle SQLi attempts…
We aren’t using it with Rails, just the activerecord core.
- Qt library, Qt designer, Qt bindings and rbuic(4)
Finally the graphic part: We are using the well knowed Qt library (which is compatible with the most common platforms, a strong asset) to create the Hardsploit interface. Using Qt and the Qt designer with Ruby requires some tweak that are explain below:
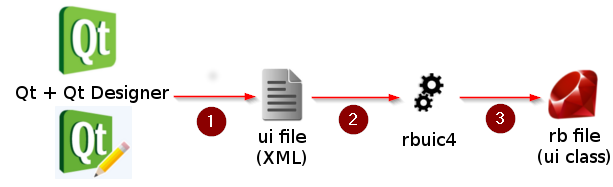 Step 1 -> Create the visual with Qt Designer, get a .ui file
Step 1 -> Create the visual with Qt Designer, get a .ui file
Step 2 -> Use rbuic to convert the ui file to Ruby:
file.ui -o file.rb
Simple as that !
HardSploit Indiegogo CrowdFunding Campaign starts now !
Our CrowdFunding Campaign for HardSploit project is started.
https://www.indiegogo.com/projects/hardsploit-like-metasploit-but-for-hardware
We will appreciated your help 😉
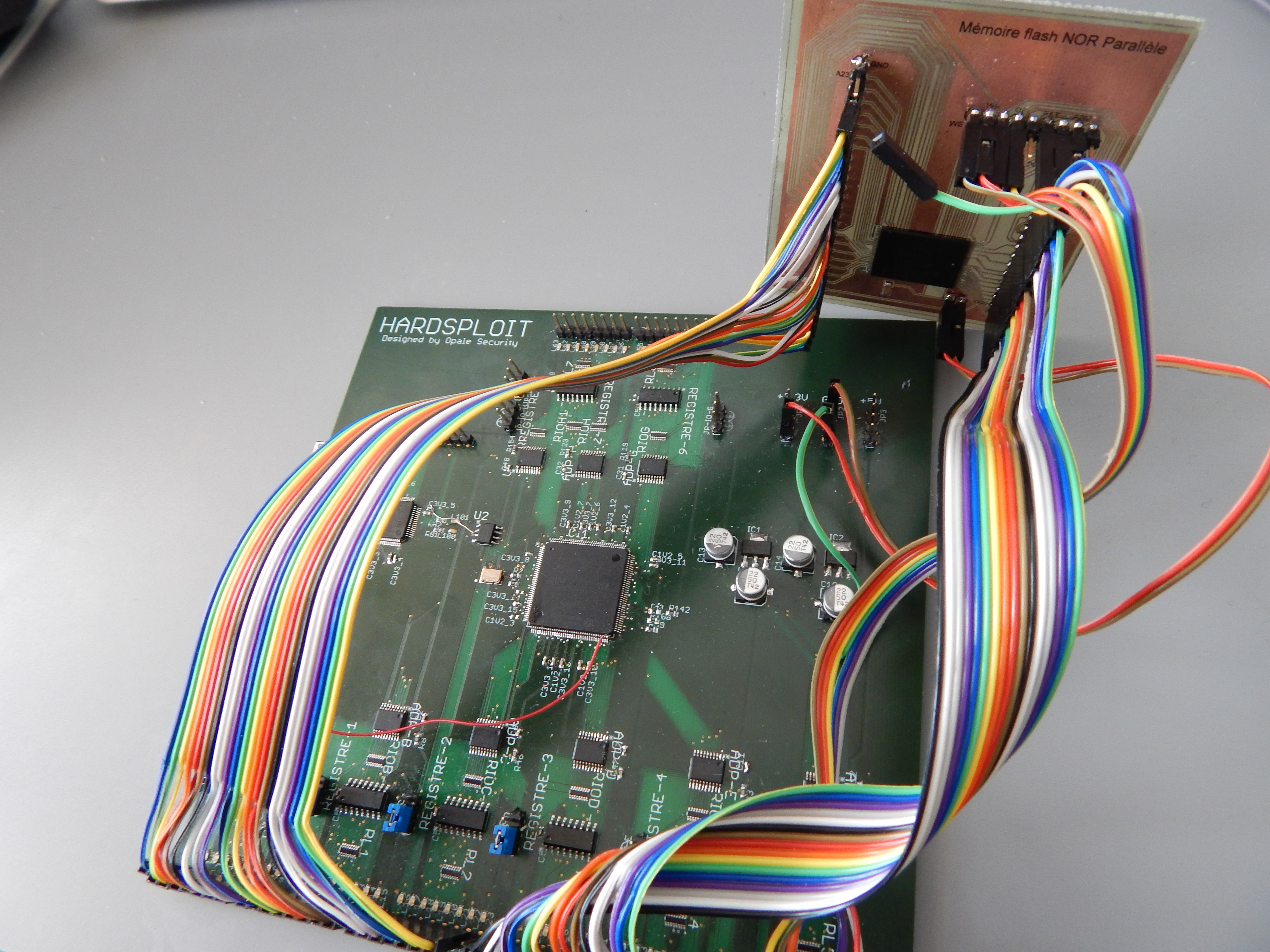
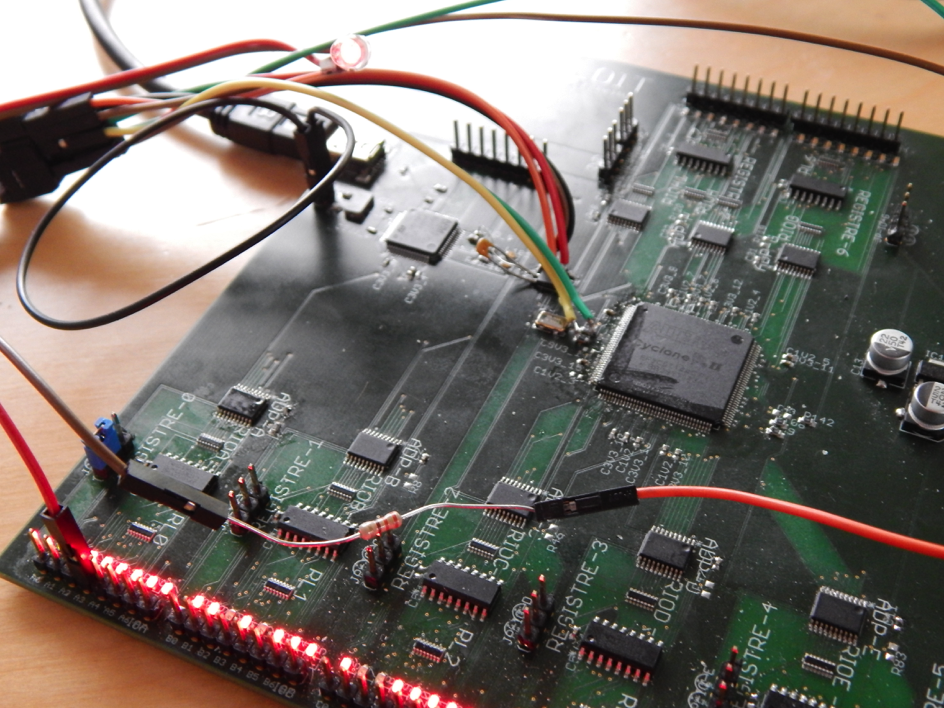
HardSploit Hardware Validated !
After few weeks of Works, we may say that the Hardsploit Hardware prototype is validated !
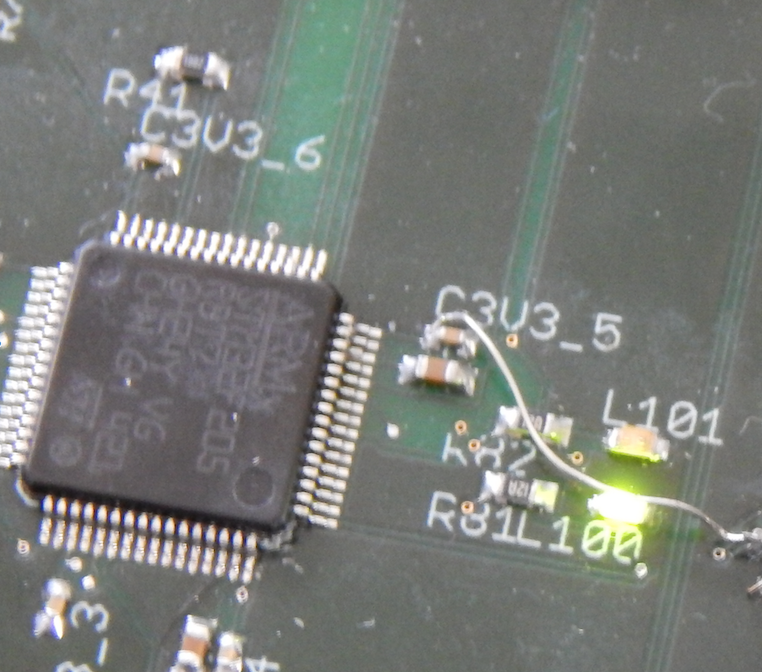
Only one wire errors 😉 see screenshot below
Simple FPGA Module update function via USB is OK. Even if Bit flipping may add some stress when you debug such sort of updating process 😉 !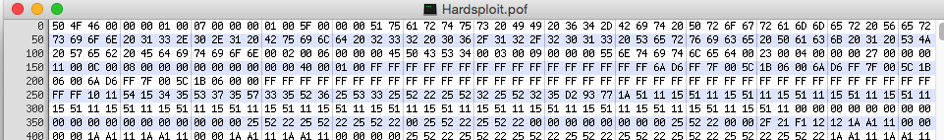
Now, if users want to scan an I2C bus, they just need to :
- Choose the VHDL module related to I2C in the GUI
- Click on Send Button
- all the VHDL code will be instantiated inside the FPGA on the HardSploit Board.
And of course Leds are working great : Visual Helping Wiring function is in development (In progress)
The HardSploit Team is ready for VHDL module development and test
- SPI sniffer, I2C Scanner, JTAG scanner etc…
Stay tuned
Soldering with our DIY reflow oven
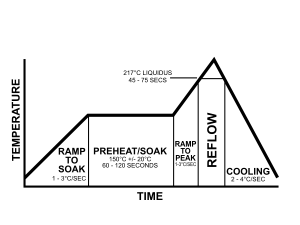
All components are now on our PCB prototype. We need to solder all Pins. Reflow soldering is the most common method for attaching surface components to a circuit board.
- Put the PCB Board in the reflow oven
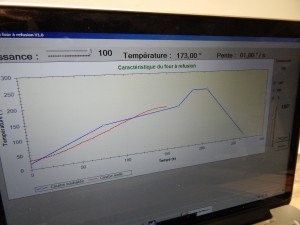
- Our Program control the inside temperature of the Reflow Oven to follow strict ramps. Theory ramps are describe below
- Theory Vs Practice 😉
- Video of Reflow oven in action (Process take around 10 mn to be completed)
- Time to find a solution to reduce the temperature when maximum is on the go.
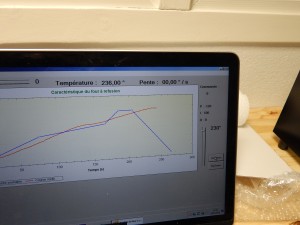
- We use a TOP SECRET process to achieve that. We open the door of the oven and try to follow the descending ramp of our GUI 😉
Videos of Pick & place all components on PCB board
After dispensing the solder past (cf last post), we begin to use the pick & place machine to put all SMT components automatically on PCB Board.
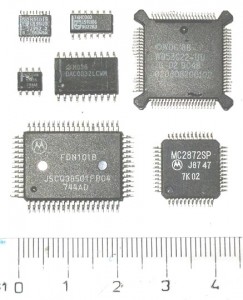
First, just remind that SMT components are (very!) small parts :
Even powerful integrated circuits are small parts : FGPA, MicroController,etc. :
After having perform all setups of the pick & place machine, we have to feed it with several tapes of SMT components:
And we installed all those tape on the Feeders of the pick&place machine
Pick & Place is ready to start
And here are the beauty of pick & place process 🙂 less than 7 mn to wait (but we cut the video for you)
Final result : all electronics component are in place on the PCB board